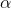question archive 1) In hypothesis testing, a Type 2 error occurs when 2) A result is called “statistically significant” whenever The p-value is larger than the significance level
1) In hypothesis testing, a Type 2 error occurs when 2) A result is called “statistically significant” whenever The p-value is larger than the significance level
Subject:MathPrice:3.87 Bought7
1) In hypothesis testing, a Type 2 error occurs when
2) A result is called “statistically significant” whenever
| The p-value is larger than the significance level. |
| The alternative hypothesis is true. |
| The null hypothesis is true. |
| The p-value is less or equal to the significance level alpha. |

Purchase A New Answer
Custom new solution created by our subject matter experts
GET A QUOTE
Answer Preview
ANSWER:
1.
In hypothesis testing, a Type 2 error occurs when "the null hypothesis is not rejected when the alternative hypothesis is true"
Explanation:
Type II error is a statistical concept used in the sense of a hypothesis test that describes an error that occurs when one supports a null hypothesis that is actually incorrect.
The mistake denies the alternative explanation, even though it is not due to chance.
2.
A result is called “statistically significant” whenever,
The p-value is less than or equal to the significance level alpha .
P-value